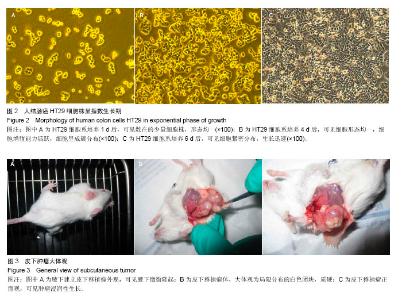
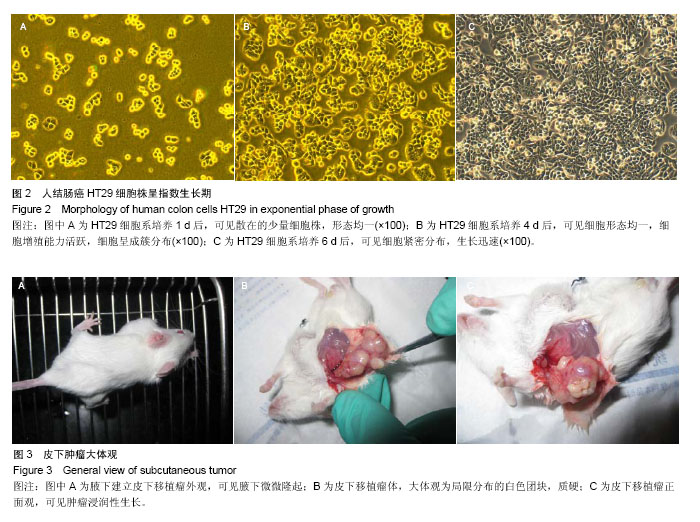
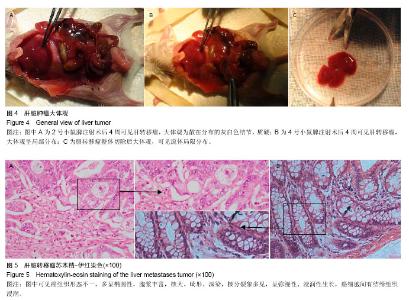
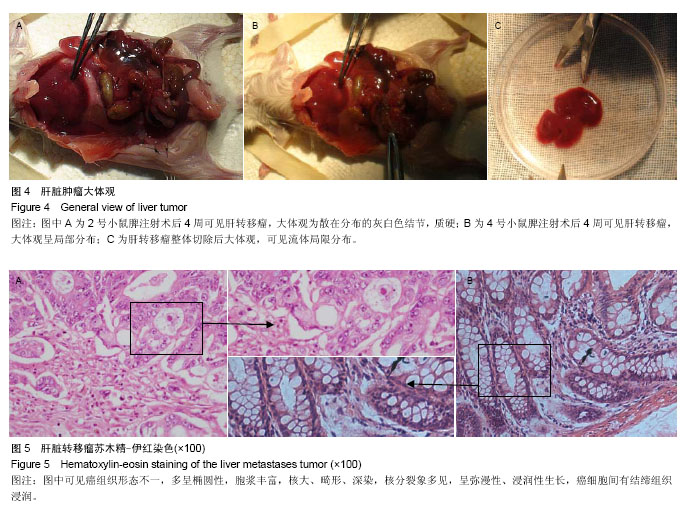
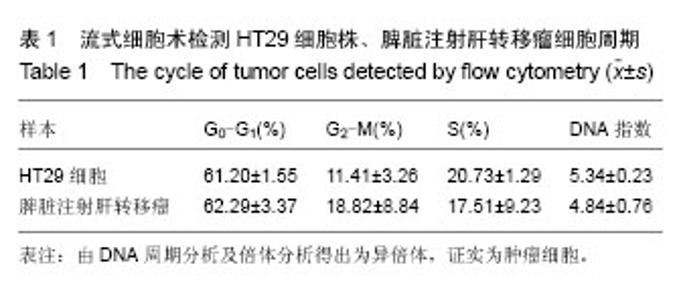
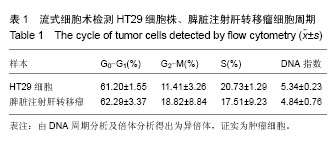
| [1] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 2012年全国卫生统计年报资料,2012: 54-55.
[2] Tan EK, Ooi LL.Colorectal cancer liver metastases - understanding the differences in the management of synchronous and metachronous disease.Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2010;39(9):719-732.
[3] Tuech JJ, Pessaux P, Regenet N, et al. Detection of occult liver metastases in colorectal cancer by measurement of biliary carcinoembryonic antigen concentration: a prospective study.J Surg Oncol. 2004;88(1):27-31.
[4] Sadahiro S, Suzuki T, Ishikawa K,et al. Recurrence patterns after curative resection of colorectal cancer in patients followed for a minimum of ten years.Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50(53):1362-1366.
[5] House MG.Safely expanding the criteria for resectability of hepatic colorectal metastases.Ann Surg. 2011;253(6):1080- 1081.
[6] Fujiwara S, Fujioka H, Tateno C, et al. A novel animal model for in vivo study of liver cancer metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(29):3875-3882.
[7] Leduc EH.Metastasis of transplantable hepatomas from the spleen to the liver in mice.Cancer Res. 1959;19:1091- 1095.
[8] Otchy D, Hyman NH, Simmang C,et al. Practice parameters for colon cancer.Dis Colon Rectum. 2004; 47(8):1269-1284.
[9] Dorrance HR, McGregor JR, McAllister EJ, et al. Bile carcinoembryonic antigen levels and occult hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer.Dis Colon Rectum. 2000; 43(9):1292-1295.
[10] Donigan M, Norcross LS, Aversa J,et al.Novel murine model for colon cancer: non-operative trans-anal rectal injection.J Surg Res. 2009;154(2):299-303.
[11] Devaud C, Rousseau B, Netzer S,et al. Anti-metastatic potential of human Vδ1(+) γδ T cells in an orthotopic mouse xenograft model of colon carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013;62(7):1199-1210.
[12] Chen HJ, Yang BL, Chen YG,et al. A GFP-labeled human colon cancer metastasis model featuring surgical orthotopic implantation.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(9):4263- 4266.
[13] Thalheimer A, Korb D, Bönicke L,et al. Noninvasive visualization of tumor growth in a human colorectal liver metastases xenograft model using bioluminescence in vivo imaging.J Surg Res. 2013;185(1):143-151.
[14] Donigan M, Loh BD, Norcross LS,et al.A metastatic colon cancer model using nonoperative transanal rectal injection. Surg Endosc. 2010;24(3):642-647.
[15] Hackl C, Man S, Francia G,et al. Metronomic oral topotecan prolongs survival and reduces liver metastasis in improved preclinical orthotopic and adjuvant therapy colon cancer models.Gut. 2013;62(2):259-271.
[16] Mathur A, Ware C, Davis L,et al. FGFR2 Is Amplified in the NCI-H716 Colorectal Cancer Cell Line and Is Required for Growth and Survival. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e98515.
[17] Kruse J, von Bernstorff W, Evert K,et al. Macrophages promote tumour growth and liver metastasis in an orthotopic syngeneic mouse model of colon cancer.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013;28(10):1337-1349.
[18] Cho YB, Hong HK, Choi YL,et al. Colorectal cancer patient-derived xenografted tumors maintain characteristic features of the original tumors.J Surg Res. 2014;187(2): 502-509.
[19] Huang X, Zou Y, Lian L,et al. Changes of T cells and cytokines TGF-β1 and IL-10 in mice during liver metastasis of colon carcinoma: implications for liver anti-tumor immunity.J Gastrointest Surg. 2013;17(7):1283-1291.
[20] Lim C, Broqueres-You D, Brouland JP,et al. Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion increases circulating bone marrow-derived progenitor cells and tumor growth in a mouse model of colorectal liver metastases.J Surg Res. 2013;184(2): 88-897.
[21] Chang YJ, Hsu WH, Chang CH,et al.Combined therapeutic efficacy of 188Re-liposomes and sorafenib in an experimental colorectal cancer liver metastasis model by intrasplenic injection of C26-luc murine colon cancer cells.Mol Clin Oncol. 2014;2(3):380-384.
[22] Langley RR, Fidler IJ.The seed and soil hypothesis revisited--the role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs.Int J Cancer. 2011;128(11): 2527-2535.
[23] Fujiwara S, Fujioka H, Tateno C,et al. A novel animal model for in vivo study of liver cancer metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(29):3875-3882.
[24] Nowakowska M, Pospiech K, Lewandowska U,et al. Diverse effect of WWOX overexpression in HT29 and SW480 colon cancer cell lines.Tumour Biol. 2014. [Epub ahead of print].
[25] Cai SR, Garbow JR, Culverhouse R,et al. A mouse model for developing treatment for secondary liver tumors.Int J Oncol. 2005;27(1):113-120.
[26] Kim HW, Cai QY, Jun HY,et al. Micro-CT imaging with a hepatocyte-selective contrast agent for detecting liver metastasis in living mice.Acad Radiol. 2008; 15(10): 1282-1290.
[27] Chowdhury S, Ongchin M, Sharratt E,et al.Intra-tumoral heterogeneity in metastatic potential and survival signaling between iso-clonal HCT116 and HCT116b human colon carcinoma cell lines.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60299.
[28] 杨剑锋,张森,高枫,等.结直肠癌肝转移动物模型的建立[J].结直肠肛门外科,2009,15(3):139-143.
[29] 袁岱岳,郭忠莹,赵任,等.人结肠癌裸鼠肝转移模型的建立[J].肿瘤防治研究,2011,38(1):28-30.
[30] 朱薇莹,张学利,陈宗佑,等.小鼠结肠癌肝转移模型的建立及其活化肝星状细胞的表达[J].复旦学报:医学版,2010,37(3): 274-277.
[31] Hwang JE, Shim HJ, Park YK,et al. Intravenous KITENIN shRNA injection suppresses hepatic metastasis and recurrence of colon cancer in an orthotopic mouse model.J Korean Med Sci. 2011;26(11):1439-1445.
[32] Pastor F, Kolonias D, Giangrande PH,et al. Induction of tumour immunity by targeted inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Nature. 2010;465(7295):227-230.
[33] Maawy AA, Hiroshima Y, Zhang Y,et al. Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Linked to Near Infrared (NIR) Dyes Conjugated to Chimeric Anti-Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Antibody Enhances Imaging of Liver Metastases in a Nude-Mouse Model of Human Colon Cancer.PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97965.
[34] Urosevic J, Garcia-Albéniz X, Planet E,et al. Colon cancer cells colonize the lung from established liver metastases through p38 MAPK signalling and PTHLH.Nat Cell Biol. 2014; 16(7):685-694.
[35] Lafreniere R, Rosenberg SA.A novel approach to the generation and identification of experimental hepatic metastases in a murine model.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986;76(2): 309-322.
[36] 左国华,葛海燕.人结肠癌裸小鼠肝转移模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,1999,16(4):373.
[37] 黄平,楼荣灿,张学栋,等.脾切除法建立人结肠癌细胞肝转移模型[J].上海实验动物科学,1999,19(3):137-139.
[38] Nano R, Barni S, Chiari P,et al. Efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy on liver metastases of colon adenocarcinoma: optical and ultrastructural study in the rat.Oncol Rep. 2004; 11(1):149-153.
[39] 杨扬,李乃卿,李兰芳,等.两种小鼠结肠癌肝转移造模方法的比较[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2008,14(4):53-55.
[40] 吴振杰,张森,欧阳君,等.两种异位种植结肠癌肝转移动物模型的比较[J].结直肠肛门外科,2012,18(1):4-7. |